SUB-NETTING: –
Subnetting is a process of dividing these large complex IP addresses into the different IP ranges. This technique is used within the network so that the wastage of IP addresses could be controlled.
Major Advantage of the Sub-Netting are: –
- Easy to Manage.
- Easy to troubleshoot.
- Reduce the wastage of IP addresses.
Types of Sub-Netting: –
- FLSM: – Fixed Length Subnet Mask.
- VLSM: – Variable Length Subnet Mask.
- Fixed Length Subnet Mask: –
Subnetting is based upon net id portion bits. In this case we need to borrow some bits from host id portion bits.That depends upon the number of subnets or networks.
Steps for Fixed Length Subnet Mask.
- How many networks or subnets=2X
X is the number of marked bits
For Ex: – 11100001 : – In this marked bits is total number of 1 in bits.
- How many host each networks=2Y-2=
Y is the number of un-marked bits
For Ex: – 11100001: – In this un-marked bits is total number of 0 in bits.
- What is valid subnet=256-Subnetmask
- What is network address?
- What is valid IP address?
- What is broadcast address?
- Variable Length Subnet Mask: –
A fixed-length subnet mask (FLSM) is a sequence of numbers of unchanging length that streamlines packet routing within the subnet of a proprietary network. A subnet can be a geographically defined local area network (LAN). Alternatively, a subnet may define security boundaries, departmental boundaries, multicast zones or hardware security parameters.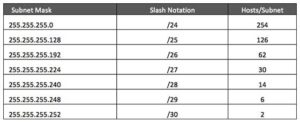
PIC: – Notations of classes.